Amplitude Modulation (AM) is among the earliest and most fundamental methods in wireless communication. It set the stage for long-distance audio broadcasting, taking the place of previous spark-gap transmitters. Whether you are an electronics student or a hobbyist dealing with RF circuits, grasping the principles of AM, both in theory and practice, is crucial. This tutorial will guide you through the concepts of AM, waveforms, circuit design, and testing it using an oscilloscope.
What is Modulation?
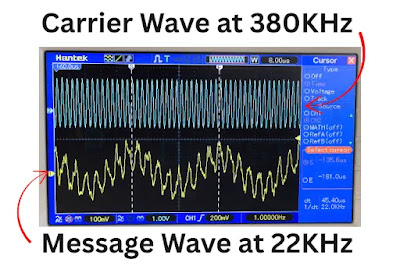
Modulation is the process of adding a low-frequency message signal, like audio, to a high-frequency carrier signal. This allows the signal to travel longer distances more efficiently. There are three primary types of analog modulation:
- Amplitude Modulation (AM)
- Frequency Modulation (FM)
- Phase Modulation (PM)
Materials Required
- BC547 - 1
- 7805 - 1
- Resistor - 470Ω - 3
- Resistor - 100Ω - 1
- Resistor 1KΩ - 1
- Capacitor - 470nF-2
- Capacitor - 10pF-1
For a more detailed Explanation and Schematics : What is Amplitude Modulation? Complete Guide with Formula, Circuit Diagram & Practical Demo



No comments:
Post a Comment