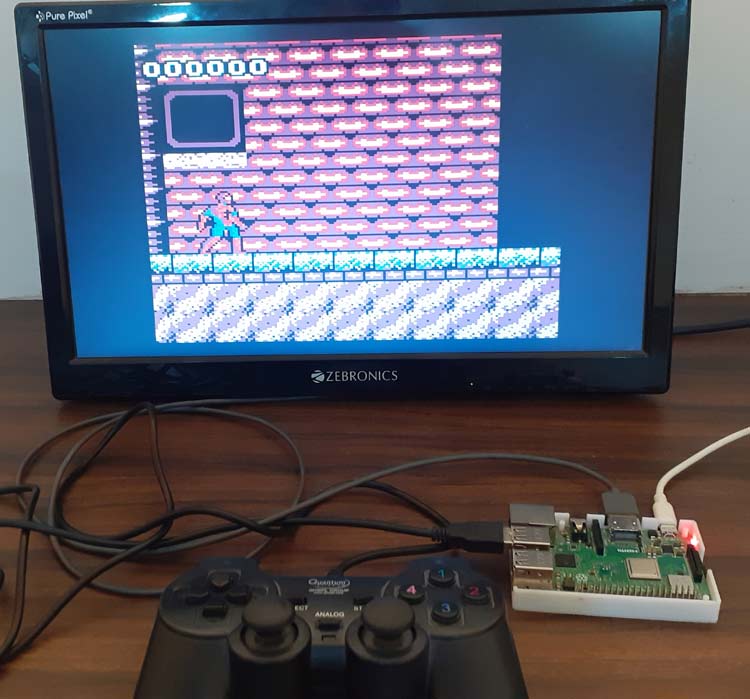
See below links for the complete project tutorials:
Friday, 13 December 2019
Sunday, 24 November 2019
ESP32 Camera Module for Video Streaming and Face Recognition
In this project a Face Recognition System is build using ESP32-CAM which can also be used as an ESP32-CAM Security system by recognizing the face of unauthorized persons. ESP32-CAM is a very small camera module with the ESP32-S chip which makes it easier to build a face recognition system without using any complex programming and any extra components.
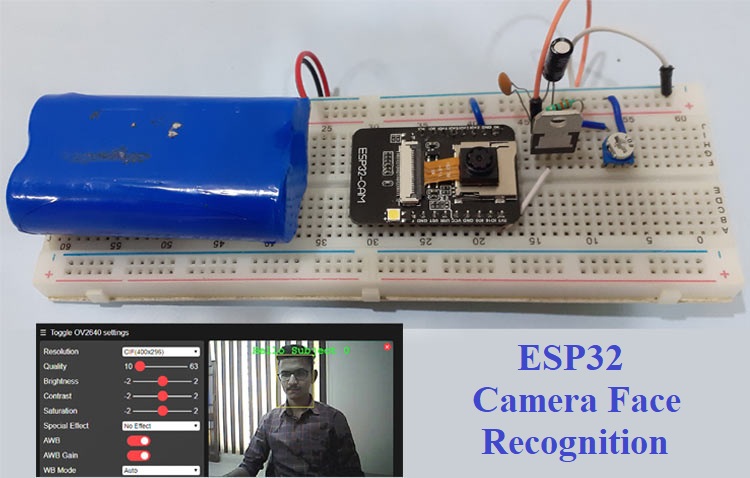
Watch the video below for a full demonstration of this ESP32-CAM security system:
View the full project article on Circuit Digest

Watch the video below for a full demonstration of this ESP32-CAM security system:
View the full project article on Circuit Digest
Wednesday, 25 September 2019
How to Build a Smart Plug using ESP8266 to Control Your Home Appliances ...
In this project I will show you how you can build your very own Smart plug using ESP8266 Wi-Fi module. The device that we built can easily be plugged into any exiting AC socket and then on the other end you can connect the actual load simply by plugging it into this socket on our device. After that just keep the main switch of your socket always on, and you can control your Load directly from your Smartphone.
Check out the full DIY tutorial here with necessary circuit diagrams and codes: https://circuitdigest.com/microcontroller-projects/diy-smart-plug-using-esp8266
Thursday, 29 August 2019
Control NEMA 17 Stepper Motor with Arduino and DRV8825 Stepper Motor Dri...
To learn more about NEMA 17 stepper motors and how to control it using Arduino and DRV8825 stepper motor driver, visit this tutorial: https://circuitdigest.com/microcontroller-projects/control-nema-17-stepper-motor-with-arduino-using-drv8825-stepper-motor-driver
Tuesday, 27 August 2019
DIY Arduino Based Musical Fountain
In this project we make an Arduino based musical water fountain which can sprinkle water according to the music beats. A sound sensor is used to recognize the music and then a DC motor to work according to the signals received by the sound sensor.
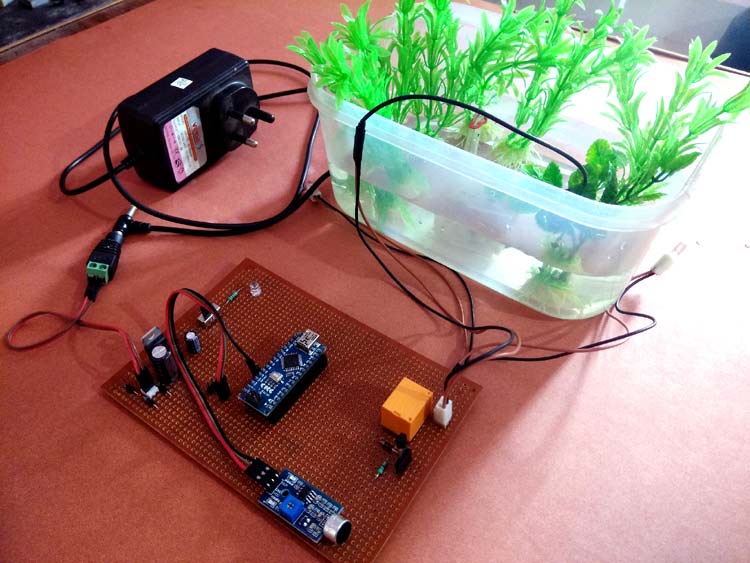

This Arduino Water Fountain takes input from any external sound source such as mobile phone and laptop and then the sound is break down to different voltage ranges, then use the output to turn on various Relay. We first used a condenser mic based sound sensor module to perform on the sound source to split the sounds into different voltage ranges. Then the voltage will be fed to op-amp to compare sound level with a particular limit. The higher voltage range will correspond to a relay switch ON which comprises a musical water fountain operating to the beats and rhythms of the song.

This Arduino Water Fountain takes input from any external sound source such as mobile phone and laptop and then the sound is break down to different voltage ranges, then use the output to turn on various Relay. We first used a condenser mic based sound sensor module to perform on the sound source to split the sounds into different voltage ranges. Then the voltage will be fed to op-amp to compare sound level with a particular limit. The higher voltage range will correspond to a relay switch ON which comprises a musical water fountain operating to the beats and rhythms of the song.
You can find the full DIY project here with required instructions along with circuits and programming.
Tuesday, 20 August 2019
DIY Raspberry Pi Based NAS Server
Raspberry Pi is the pocket sized computer having almost all the feature of a normal computer including USB port, LAN port, audio/video output, HDMI port etc. It also has inbuilt Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity which makes it perfect candidate to build various online servers like Webserver, Media server, Print Server, Plex server etc. So here we will be creating another server using Raspberry Pi- File Server or NAS (Network Attached Storage), where you can plug any storage device with Raspberry Pi and access it using any computer connected on the same network.
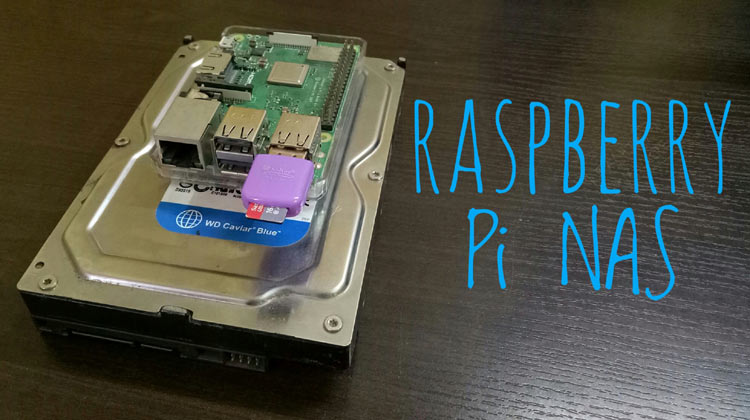
Using this Raspberry Pi NAS server you can share and access the files and folders without actually connecting the storage device to your system.
In this tutorial, we will install Samba in preinstalled Raspbian OS, so you don’t have to loose the default Raspbian OS. Samba is a re-implementation of the SMB (Server Message Block) networking protocol which integrates Linux computers with MAC and Windows based systems. There is another protocol named CIFS (Common Internet File System) which is an implementation of the SMB protocol. Nowadays, CIFs or SMB is used interchangeably, but most people use the term SMB.
Check out the full DIY tutorial here
In this tutorial, we will install Samba in preinstalled Raspbian OS, so you don’t have to loose the default Raspbian OS. Samba is a re-implementation of the SMB (Server Message Block) networking protocol which integrates Linux computers with MAC and Windows based systems. There is another protocol named CIFS (Common Internet File System) which is an implementation of the SMB protocol. Nowadays, CIFs or SMB is used interchangeably, but most people use the term SMB.
Check out the full DIY tutorial here
Thursday, 8 August 2019
DIY Raspberry Pi Gaming Console using RetroPie
Raspberry Pi is an amazing credit-card sized computer most suited for IoT based applications and online servers like Print server, webserver, Media server. Many types of custom ROMs and custom operating systems are available for Raspberry Pi and you just need to burn the custom ROM on SD card and insert it in Raspberry Pi. Like Windows 10 and Android can be easily installed on Raspberry Pi.
Monday, 3 June 2019
DIY IoT Based Biometric Attendance Project using Arduino
In this project we use IoT to make attendance system more useful and online accessible. Most of the attendance systems generally store the information over a micro SD card and have to be connected to software via a computer to access the information.
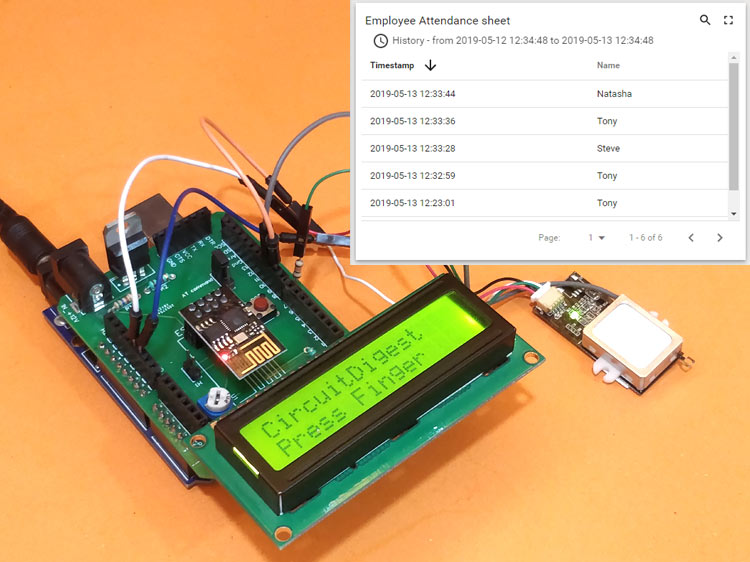

So here we use Arduino and an IoT platform called Thingsboard to build a biometric attendance system that scans for fingerprint and on successful identification of the person it will log the information to the cloud platform ThingsBoard by using the ESP8266 Wi-Fi module. This information can then be displayed in the dashboard of ThingsBoard making it available for the required authorities to view and analysis information over the internet without having any direct physical access to the hardware.
Interesting? Follow this Circuit Digest tutorial to make this biometric attendance system project.
Below is the demonstration video of the project:

So here we use Arduino and an IoT platform called Thingsboard to build a biometric attendance system that scans for fingerprint and on successful identification of the person it will log the information to the cloud platform ThingsBoard by using the ESP8266 Wi-Fi module. This information can then be displayed in the dashboard of ThingsBoard making it available for the required authorities to view and analysis information over the internet without having any direct physical access to the hardware.
Interesting? Follow this Circuit Digest tutorial to make this biometric attendance system project.
Below is the demonstration video of the project:
Tuesday, 9 April 2019
Interfacing a Camera Module with Arduino Uno
In this DIY project a OV7670 camera module is interfaced with Arduino UNO to click and store images.

The OV7670 camera module works on 3.3V, so it becomes important to avoid Arduino which gives 5V output at their Output GPIO pins. The OV7670 is a FIFO camera. But in this tutorial, the picture or frames will be grabbed without FIFO.
Below are some of the pictures captured using the above shown hardware.


Check out the complete tutorial on below link:
https://circuitdigest.com/microcontroller-projects/how-to-use-ov7670-camera-module-with-arduino
Tuesday, 5 March 2019
Digital Wall Clock using Atmega16 and DS3231 RTC
This is a DIY PCB project for a Digital wall clock, which is made using Atmega16 microcontroller and DS3231 RTC module.
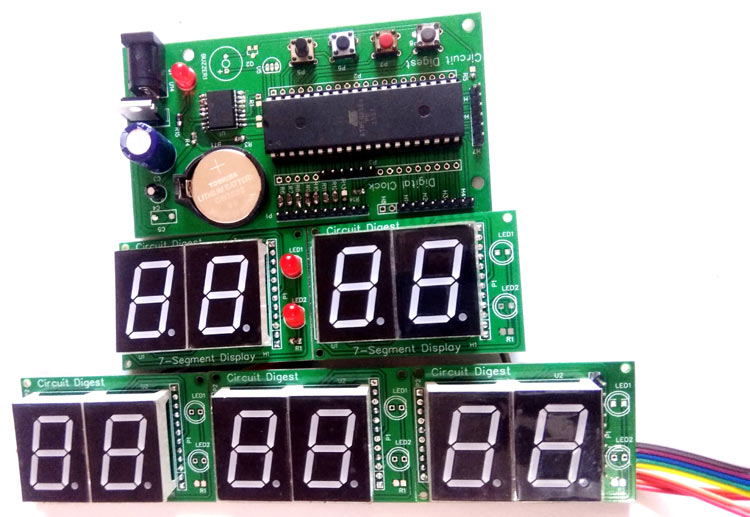
In this Digital Clock Project, ten common anode 7-segment displays of 0.8-inch are used to display time and date. Here seven segment displays are used to show hour, minute, date, month and year. Our PCB design also has options to display seconds and temperature, which can be displayed by adding more display units.
For complete project, check out the link below: https://circuitdigest.com/microcontroller-projects/digital-wall-clock-on-pcb-using-avr-microcontroller-atmega16-and-rtc

In this Digital Clock Project, ten common anode 7-segment displays of 0.8-inch are used to display time and date. Here seven segment displays are used to show hour, minute, date, month and year. Our PCB design also has options to display seconds and temperature, which can be displayed by adding more display units.
You can watch the video below for more details of this AVR project.
For complete project, check out the link below: https://circuitdigest.com/microcontroller-projects/digital-wall-clock-on-pcb-using-avr-microcontroller-atmega16-and-rtc
Monday, 11 February 2019
Using Google Firebase with ESP8266 NodeMCU
In this DIY project will be building a project where we’ll use a temperature & humidity sensor DHT11 and a NodeMCU ESP8266 Module to log the temperature and humidity in real time on Google’s Firebase database server.
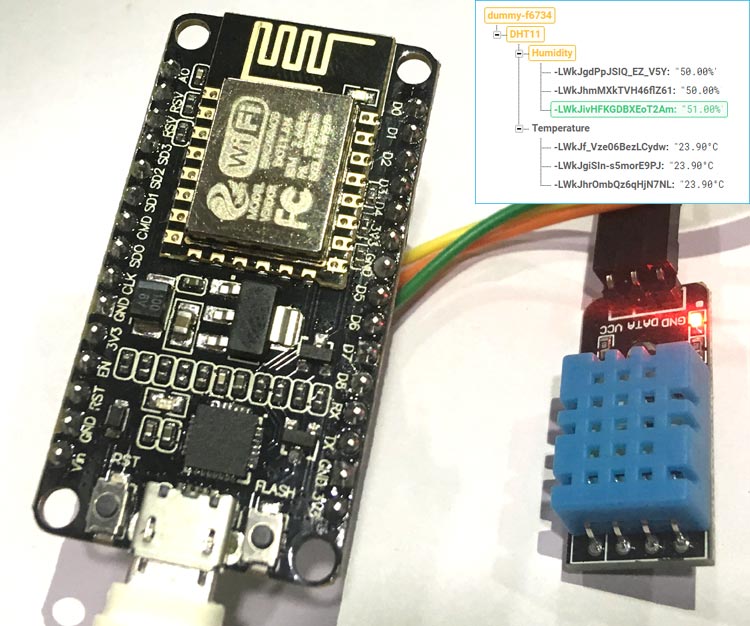
The complete project is divided into two sections. First we start with assembling the hardware components and uploading firmware into it. And second, we will use Firebase to setup with NodeMCU to exchange real time data.
Find the complete project tutorial on circuit digest: https://circuitdigest.com/microcontroller-projects/sending-temperature-and-humidity-data-to-firebase-database-using-esp8266

The complete project is divided into two sections. First we start with assembling the hardware components and uploading firmware into it. And second, we will use Firebase to setup with NodeMCU to exchange real time data.
Find the complete project tutorial on circuit digest: https://circuitdigest.com/microcontroller-projects/sending-temperature-and-humidity-data-to-firebase-database-using-esp8266
Monday, 4 February 2019
Interfacing ESP8266 with ARM7-LPC2148 and Creating a Webserver to control an LED
ESP8266 Wi-Fi transceiver provides a way to connect a microcontroller to the network. It is widely used in IoT projects as it is cheap, tiny and easy to use. This WiFi module can be used with any microcontroller to connect it with internet. In some of the following tutorials, it is used with Arduino and Raspberry pi, to create webserver such as Raspberry webserver and Arduino webserver.
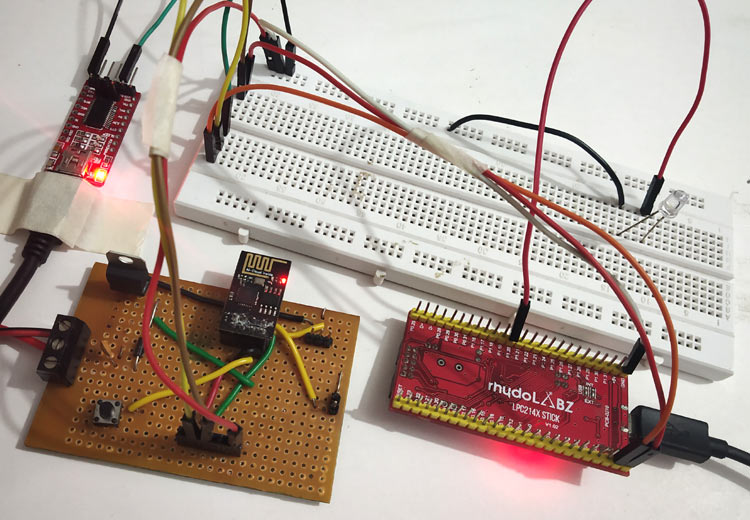
To interface an ESP8266 Module with the ARM7-LPC2148 microcontroller and create a webserver to control the LED connected to LPC2148. The workflow will go like this:
- Send AT commands from LPC2148 to ESP8266 to configure ESP8266 in AP mode
- Connect the laptop or computer Wi-Fi with the ESP8266 Access point
- Create a HTML webpage in PC with Access point IP address of the ESP8266 webserver
- Create a program for LPC2148 to control the LED according to the value received from ESP8266
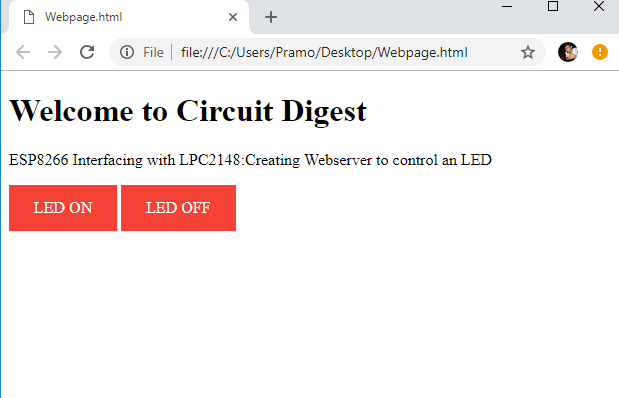
If you are completely new to ESP8266 Wi-Fi module visit the below links to get familiar with ESP8266 Wi-Fi module.
Getting Started with ESP8266 Wi-Fi Transceiver (Part 1)
Getting Started with ESP8266 (Part 2): Using AT Commands
Getting Started with ESP8266 (Part 3): Programming ESP8266 with Arduino IDE and Flashing its Memory
Getting Started with ESP8266 (Part 2): Using AT Commands
Getting Started with ESP8266 (Part 3): Programming ESP8266 with Arduino IDE and Flashing its Memory
You can check the complete tutorial to interface ESP8266 module with LPC2148: https://circuitdigest.com/microcontroller-projects/iot-based-ARM7-LPC2148-webserver-to-control-an-led
Wednesday, 23 January 2019
What is MOSFET and Where are they Used?
MOSFET is basically a transistor which uses field effect. MOSFET stands for Metal Oxide Field Effect Transistor, which has a gate. The gate voltage determines the conductivity of the device. Depending on this gate voltage we can change the conductivity and thus we can use it as a switch or as an amplifier like we use Transistor as a switch or as an amplifier.
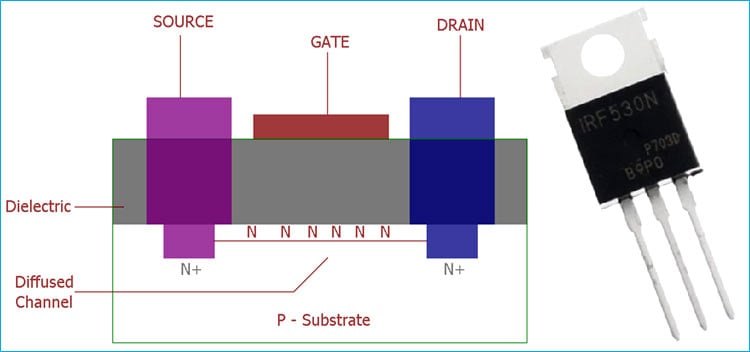
MOSFET provides very high input impedance and it is very easy to bias. So, for a linear small amplifier, MOSFET is an excellent choice. The linear amplification occurs when we bias the MOSFET in the saturation region which is a centrally fixed Q point.
Check out the following article to learn more about MOSFETs

MOSFET provides very high input impedance and it is very easy to bias. So, for a linear small amplifier, MOSFET is an excellent choice. The linear amplification occurs when we bias the MOSFET in the saturation region which is a centrally fixed Q point.
Check out the following article to learn more about MOSFETs
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)